Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent

Newsweek
Grasp current events and learn more about batteries
Exploring Various Types of Lithium Batteries: Characteristics, Advantages, and Applications
Types of Lithium Batteries and Their Advantages
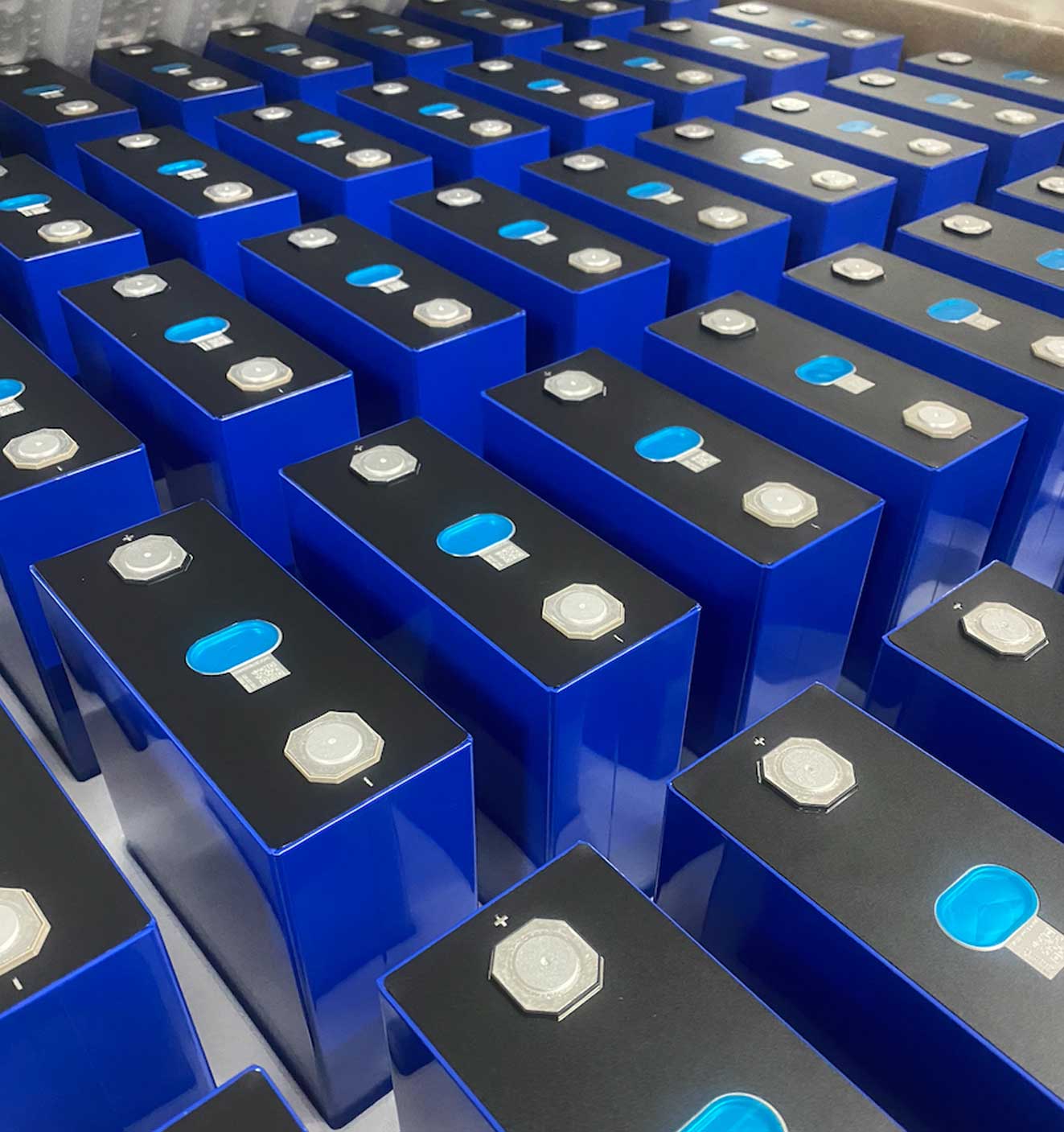
Lithium batteries are essential energy storage devices widely used in various electronic devices and electric vehicles. With technological advancements, several types of lithium batteries have emerged, each with its unique advantages and suitable applications. In this article, I will detail several main types of lithium batteries, including Lithium-ion (Li-ion), Lithium Polymer (LiPo), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4), etc., and delve into their characteristics, advantages, and application areas.
1. Lithium-ion Batteries (Li-ion)
Lithium-ion batteries are one of the most widely used types of lithium batteries, characterized by:
- High Energy Density: Compared to traditional nickel-cadmium and nickel-metal hydride batteries, lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, providing longer operating times.
- Lightweight: Lithium-ion batteries have a lighter weight, suitable for products requiring lightweight designs such as portable electronic devices, drones, etc.
- No Memory Effect: There is no memory effect in lithium-ion batteries, allowing users to charge them as needed without fully discharging them first.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate: Lithium-ion batteries have a relatively low self-discharge rate, allowing them to retain charge for extended periods when idle.
Applications include but are not limited to smartphones, tablets, laptops, power tools, etc.
2. Lithium Polymer Batteries (LiPo)
Lithium Polymer batteries are a specialized form of lithium-ion batteries, known for:
- Flexible Design: Lithium Polymer batteries can use flexible polymer materials as electrolytes, allowing for free-form designs based on product shape and size requirements, suitable for products like curved displays.
- High Discharge Rate: LiPo batteries have a high discharge rate, capable of rapidly releasing energy, making them suitable for devices with high power requirements like remote-controlled models, electric vehicles, etc.
- Thin Form Factor: Compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, LiPo batteries have a thinner profile, making them suitable for products with strict size constraints.
Applications include but are not limited to drones, electric toys, wearable devices, etc.
3. Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries (LiFePO4)
Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries represent a relatively newer lithium battery technology, known for:
- High Safety: LiFePO4 batteries use lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, offering enhanced chemical stability and safety compared to other lithium battery types, reducing the risk of overheating or fires.
- Long Cycle Life: LiFePO4 batteries have a long cycle life, capable of enduring more charge-discharge cycles, making them suitable for applications with high battery life requirements such as solar energy storage systems, electric vehicles, etc.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range: LiFePO4 batteries exhibit a wider operating temperature range compared to other lithium batteries, maintaining good performance even in extreme temperature environments.
Applications include but are not limited to solar energy storage systems, electric vehicles, electric bicycles, etc.
4. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
Lithium Iron Phosphate batteries share similarities with LiFePO4 batteries but have some minor differences. Their advantages include:
- Long Cycle Life: Similar to other lithium batteries, LFP batteries offer a long cycle life, enduring multiple charge-discharge cycles, making them suitable for long-term use scenarios.
- High Safety: LFP batteries exhibit high safety levels with enhanced chemical stability, reducing the likelihood of safety incidents.
Applications include electric vehicles, solar energy storage systems, Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS), etc.
5. Lithium Manganese Oxide Batteries (LMO)
Lithium Manganese Oxide batteries are another common type of lithium battery, characterized by:
- High Power Output: LMO batteries offer high power output capabilities, enabling rapid energy release, suitable for applications requiring high power.
- Good Stability: LMO batteries demonstrate good chemical stability, maintaining performance stability over extended periods of use.
- Environmental Friendliness: LMO batteries are considered environmentally friendly due to their lower content of toxic materials such as cobalt, making them a preferred choice in certain applications.
Applications include but are not limited to power tools, medical devices, electric vehicles, etc.
In conclusion, each type of lithium battery offers distinct advantages and is suitable for different applications based on factors such as energy density, power output, safety, and cycle life requirements. Understanding the characteristics of each type is crucial for selecting the most suitable battery technology for specific use cases.


